Sodium Ion Technology will provide you with many benefits. Its energy is derived from one of the most clean and common materials on the planet ‒ salt (Sodium Chloride = NaCl). Its performance exceeds any lead battery and is like a lithium battery.
However, it is different in some key areas, chiefly it does not suffer from very cold or very hot temperatures, and crucially, it does not suffer from thermal runaway, which results in battery fires.
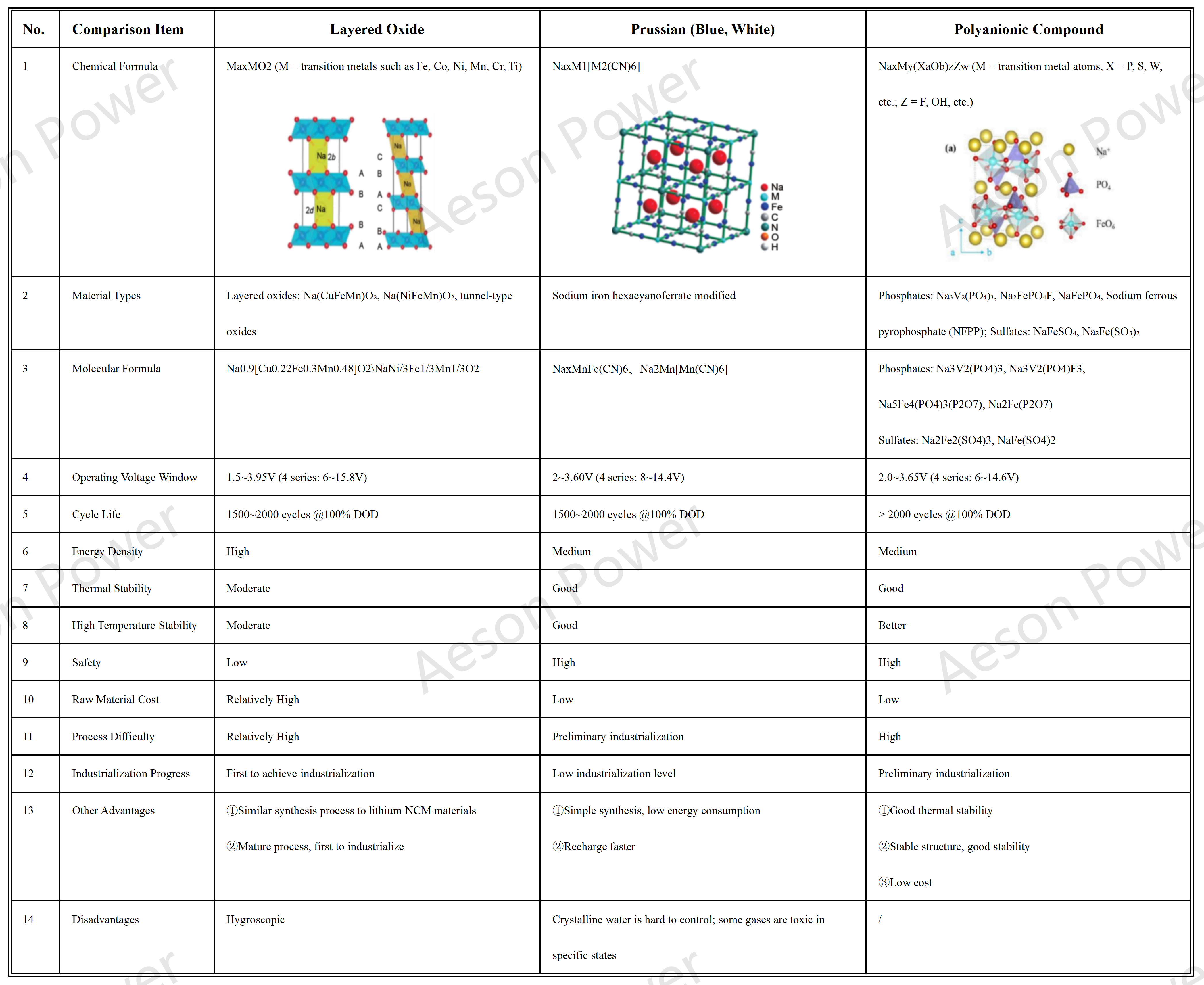
Technical Landscape of Mainstream Cathode Materials
Positive Electrode Technology Routes | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Layered Oxides (NFM) | High energy density | Poor safety, high cost, and poor cycle life |
| Polyanion Compounds(NFPP) | Good cycle life | Low energy density |
| Prussian Blue Analogs (PBA) | High energy density | Difficulty in removing moisture during manufacturing and toxic gases generated under specific conditions |
Lead-Acid, Lithium, and Sodium-lon Batteries Comparison
| Lead Acid= Pb | LFP | NMC | NFPP | |
| Energy Density(Wh/kg) | 30~50 | 120~200 | 200~300 | 100~130 |
| Cycle Life | >700 | 5000~6000 | 2500~5000 | >5000 |
| Voltage Range | 1.5~2.4V | 2.5~3.65V | 2.8~4.3V | 1.5~3.65V |
| High-Temperature Performance | Moderate | Moderate | Poor | Good |
| Low-Temperature Performance | Poor | Poor | Good | Good |
| Cost | Low | Relatively High | High | Low |
Pouch Cell Composition / NFPP
(-) C | NaPF6 | Na4Fe3(P2O7)(PO4)2 (+)
| Items | Materials | Functions |
| Positive | Na4Fe3(P2O7)(PO4)2 (NFPP) | Provide Na+ that migrate and embed into the negative electrode during charging |
| Negative | C (High porosity) | Receive and store sodium ions, return/embed into the positive electrode during discharge |
| Electrolyte | NaPF6 | Provide channels and reaction interfaces for sodium ion transport |
| Separator | PP or PE | Isolating the positive and negative electrodes, avoiding direct short circuit, while allowing Sodium ions to pass through |
| Package | (PP+AL+Nylon) | Sealing the battery as a whole, isolating the interior of the battery cellfrom the environment |
| Terminal | AI | Connect the battery to the external circuit/load |